Mini Tensorflow example
| 操作組 | 操作 |
|---|---|
| Maths | Add, Sub, Mul, Div, Exp, Log, Greater, Less, Equal |
| Array | Concat, Slice, Split, Constant, Rank, Shape, Shuffle |
| Matrix | MatMul, MatrixInverse, MatrixDeterminant |
| Neuronal Network | SoftMax, Sigmoid, ReLU, Convolution2D, MaxPool |
| Checkpointing | Save, Restore |
| Queues and syncronizations | Enqueue, Dequeue, MutexAcquire, MutexRelease |
| Flow control | Merge, Switch, Enter, Leave, NextIteration |
TensorFlow的算術操作如下:
| 操作組 | 操作 | |
|---|---|---|
| tf.add(x, y, name=None) | 求和 | |
| tf.sub(x, y, name=None) | 減法 | |
| tf.mul(x, y, name=None) | 乘法 | |
| tf.div(x, y, name=None) | 除法 | |
| tf.mod(x, y, name=None) | 取模 | |
| tf.abs(x, name=None) | 求絕對值 | |
| tf.neg(x, name=None) | 取負 (y = -x). | |
| tf.sign(x, name=None) | 返回符號 y = sign(x) = -1 if x < 0; 0 if x == 0; 1 if x > 0. | |
| tf.inv(x, name=None) | 取反 | |
| tf.square(x, name=None) | 計算平方 (y = x * x = x^2). | |
| tf.round(x, name=None) | 舍入最接近的整數 # ‘a’ is [0.9, 2.5, 2.3, -4.4] tf.round(a) ==> [ 1.0, 3.0, 2.0, -4.0 ] |
|
| tf.sqrt(x, name=None) | 開根號 (y = \sqrt{x} = x^{1/2}). |
|
| tf.pow(x, y, name=None) | 冪次方 # tensor ‘x’ is [[2, 2], [3, 3]] # tensor ‘y’ is [[8, 16], [2, 3]] tf.pow(x, y) ==> [[256, 65536], [9, 27]] |
|
| tf.exp(x, name=None) | 計算e的次方 | |
| tf.log(x, name=None) | 計算log,一個輸入計算e的ln,兩輸入以第二輸入為底 | |
| tf.maximum(x, y, name=None) | 返回最大值 (x > y ? x : y) | |
| tf.minimum(x, y, name=None) | 返回最小值 (x < y ? x : y) | |
| tf.cos(x, name=None) | 三角函數cosine | |
| tf.sin(x, name=None) | 三角函數sine | |
| tf.tan(x, name=None) | 三角函數tan | |
| tf.atan(x, name=None) | 三角函數ctan |
張量操作Tensor Transformations
####數據類型轉換Casting
| 操作組 | 操作 |
|—————————-|——————————————————|
| tf.string_to_number | |
| (string_tensor, out_type=None, name=None) | 字符串轉為數字 |
| tf.to_double(x, name=’ToDouble’) | 轉為64位浮點類型–float64 |
| tf.to_float(x, name=’ToFloat’) | 轉為32位浮點類型–float32 |
| tf.to_int32(x, name=’ToInt32’) | 轉為32位整型–int32 |
| tf.to_int64(x, name=’ToInt64’) | 轉為64位整型–int64 |
| tf.cast(x, dtype, name=None) | 將x或者x.values轉換為dtype |
| # tensor a is [1.8, 2.2], dtype=tf.float | |
| tf.cast(a, tf.int32) ==> [1, 2] # dtype=tf.int32 | |
形狀操作Shapes and Shaping
| 操作組 | 操作 | |
|---|---|---|
| tf.shape(input, name=None) | 返回數據的shape # ‘t’ is [[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]], [[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]]] shape(t) ==> [2, 2, 3] |
|
| tf.size(input, name=None) | 返回數據的元素數量 # ‘t’ is [[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]], [[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]]]] size(t) ==> 12 |
|
| tf.rank(input, name=None) | 返回tensor的rank 注意:此rank不同於矩陣的rank, tensor的rank表示一個tensor需要的索引數目來唯一表示任何一個元素 也就是通常所説的 “order”, “degree”或”ndims” #’t’ is [[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]], [[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]]] # shape of tensor ‘t’ is [2, 2, 3] rank(t) ==> 3 |
|
| tf.reshape(tensor, shape, name=None) | 改變tensor的形狀 # tensor ‘t’ is [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] # tensor ‘t’ has shape [9] reshape(t, [3, 3]) ==> [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]] #如果shape有元素[-1],表示在該維度打平至一維 # -1 將自動推導得為 9: reshape(t, [2, -1]) ==> [[1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6]] |
|
| tf.expand_dims(input, dim, name=None) | 插入維度1進入一個tensor中 #該操作要求-1-input.dims() # ‘t’ is a tensor of shape [2] shape(expand_dims(t, 0)) ==> [1, 2] shape(expand_dims(t, 1)) ==> [2, 1] shape(expand_dims(t, -1)) ==> [2, 1] <= dim <= input.dims() |
https://hk.saowen.com/a/2766b13f38b54ab09e6d478975f5feca8abbf01d842e2ca8f5111160fcbb0e36
tf.reshape
tf.reshape(tensor,shape, name=None)
重組
|
|
降為
|
|
平坦
|
|
tf.split
tf.split(split_dim, num_split, value, name=’split’)
將大的tensor分割成更小的tensor,第一個參數代表沿著那一維開始分割,第二個參數代表切成幾段
tf.nn.max_pool
max pooling 是CNN 當中的最大值池化操作,其實用法和卷積很類似
tf.nn.max_pool(value,ksize, strides, padding, name=None)
|
|
假設有這樣一張圖,雙通道
第一個通道: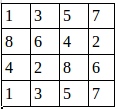
第二個通道: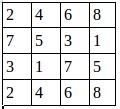
|
|
這裡步長為1 ,窗口大小2×2 ,輸出結果:
image:
|
|
池化後的圖就是:
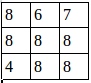
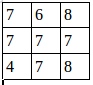
證明了程序的結果是正確的。
我們還可以改變步長
|
|